Sorting T Cell Subsets with the WOLF G2 Cell Sorter
Introduction
T cells are of great interest to researchers and clinicians because of the critical role they play in the immune system. Recently, T cells have moved from the laboratory to revolutionary therapeutics in oncology, e.g. CAR-T, as well as vaccine development. As a result, T cell subset isolation is critical to researchers as there are many different types of T cells that play different roles within the immune system. However, isolating specific T cell subsets can be challenging since it requires the use of several epitope binding antibodies.
Fluorescence-activated cell sorters are exceptionally appropriate instruments that address this challenge by allowing researchers to label cells with multiple fluorescent antibodies and easily identify different T cell subsets within a cell population. A challenge with traditional droplet-based sorters is that they use high-pressure that can result in a significant amount of shear stress and lead to low viability. Furthermore, the non-disposable fluidics of these traditional sorters can also result in confounding cross-contamination between samples or the presence of microbes that contaminate samples.
The WOLF G2 Cell Sorter is a gentle microfluidic cell sorter equipped with 2 lasers in 3 configurations: 488/405nm, 488/561nm and 488/637nm; and up to 9 fluorescent channels. In addition, the WOLF G2 has the ability to sort 2 target populations at the same time and dispense single cells into 96- or 384-well plates with the N1 Single Cell Dispenser. Most importantly, the G2 sorts cells with less than 2 psi and uses completely disposable fluidics that enable high viability and eliminate cross-contamination or microbial growth. Here we used the G2 with the 488/637nm and 488/405nm laser configurations to identify and sort CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, simultaneously.
Methods
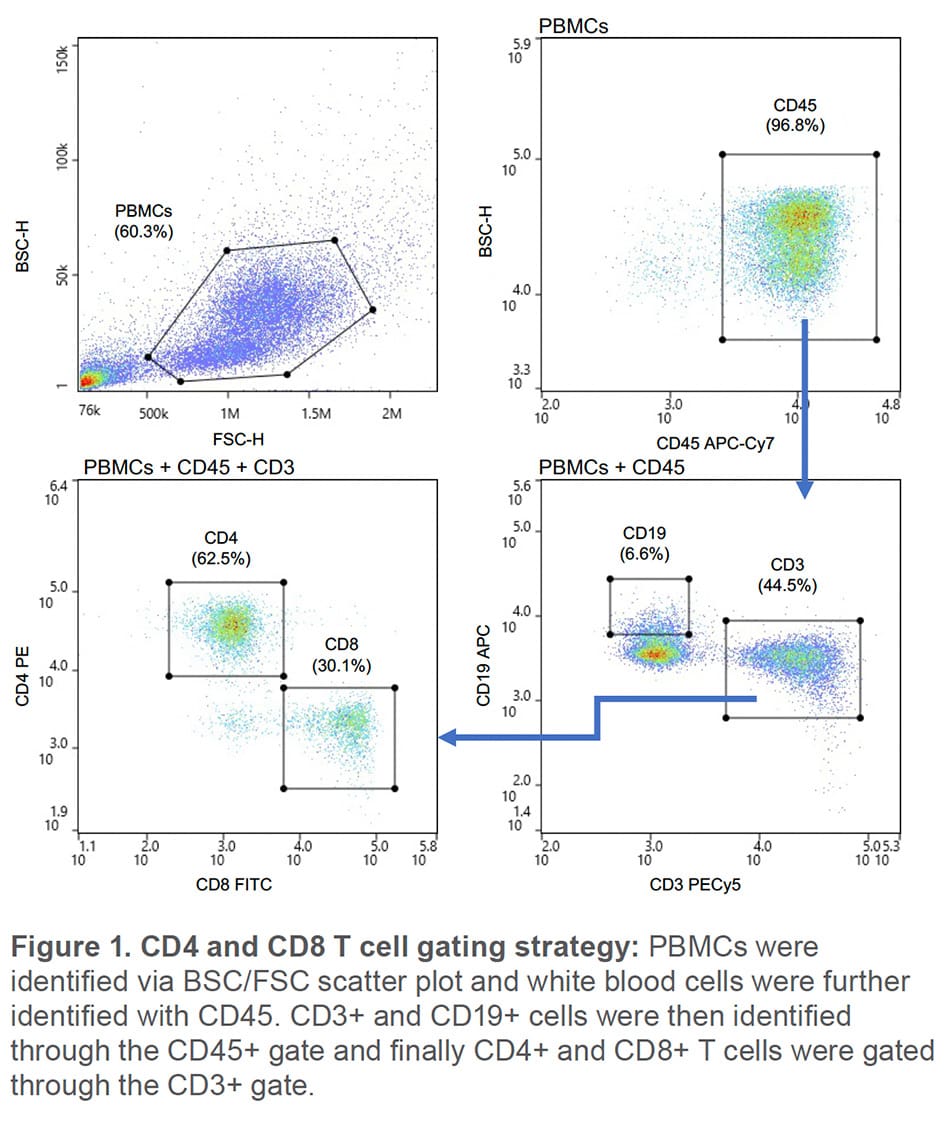
BioLegend’s Veri-Cell™ PBMCs (BioLegend, #425004) were prepared according to the manufacturer instructions and diluted in sample buffer of PBS + 1% BSA. 1 x 106 cells were resuspended in 50 μL of sample buffer and blocked with 5% True-Stain Monocyte Blocker (BioLegend, #426102) for 10 minutes at room temperature. For the 488/637nm laser configuration, cells were then stained with BioLegend antibodies CD45 APC-Cy7 (#30414), CD8 FITC (#301106), CD4 PE (300508), CD3 Pe-Cy5 (#300410), and CD19 APC (#302212). Cells were stained with CD45 Pacific Blue (#36859), CD4 AF488 (#317419), CD8 BV510 (#300933), CD3 BV570 (#300435) and CD19 PE (#302208) for the 405/488nm configuration. Following a 20-minute incubation, the samples were washed and resuspended to 500,000 cells/ mL. Single color compensation controls were also prepared. Compensation was applied to the PBMCs sample within the WOLFViewer software. T cells were identified as CD45+ CD3+ CD19- and CD4+ and CD8+ populations identified by being positive for either CD4 or CD8 (Figure 1). Both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were sorted at the same time and purity was accessed by re-analyzing the samples on the WOLF G2. This was repeated in triplicate, including the use of new cartridges and tubing sets for each replicate to eliminate potential cross contamination.
Results
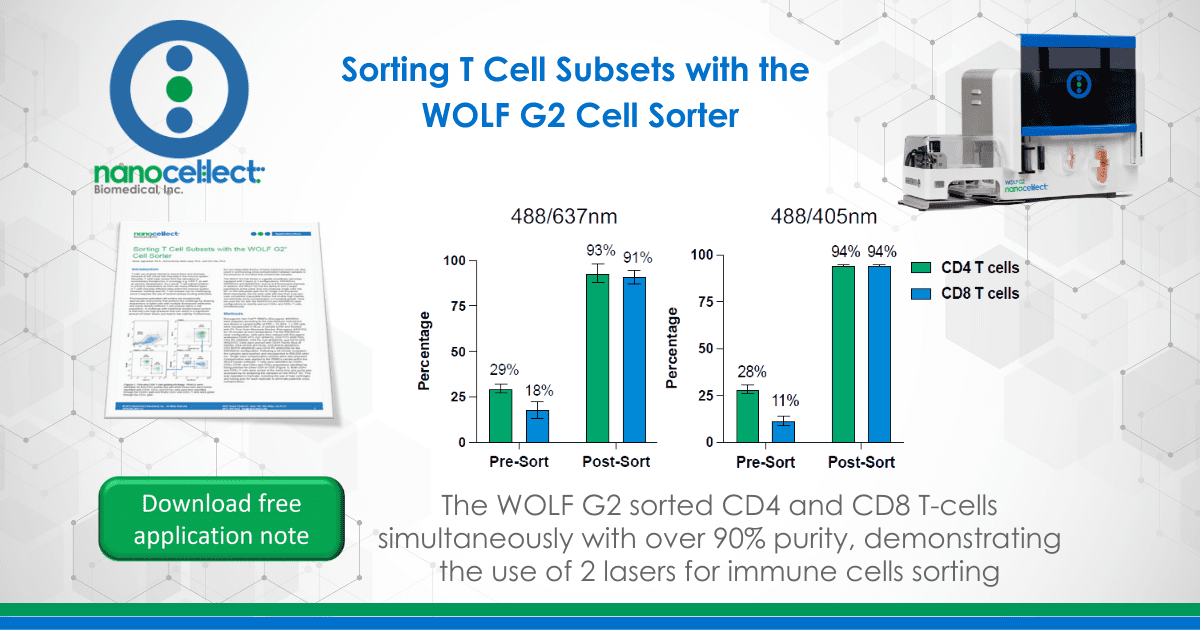
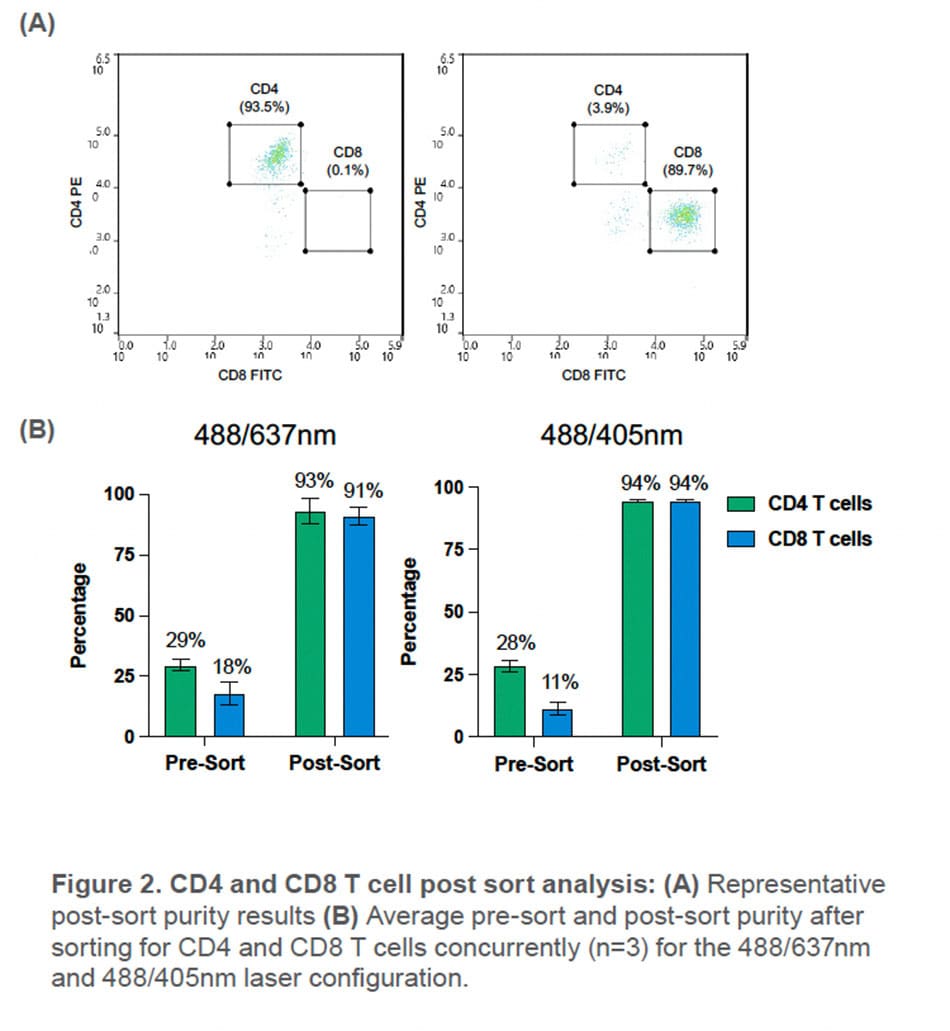
Using the WOLF G2 in the 488/637nm configuration, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were sorted with an average purity of 93 ± 5.3% and 91± 3.7%, respectively. This is a 3.2-fold enrichment of CD4 T cells and a 5-fold enrichment of CD8 T cells in the PBMC population.
With the WOLF G2 in the 488/405nm configuration, high purities of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were also observed with an average purity of 94± 2.5% and 94± 2.5% respectively. This resulted a 3.3-fold enrichment of CD4 T cells and an 8.5-fold enrichment of CD8 T cells in the PBMC population.
Conclusion
The WOLF G2 488/637nm laser configuration has up to 7 fluorescent channels and the WOLF G2 488/405nm laser configuration has up to 9 fluorescent channels along with its gentle sorting technology and disposable fluidic system. Here, 5 fluorescent markers were used to confidently identify CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from a PBMC population. Furthermore, sorting both the CD4+ and CD8+ T cells simultaneously resulted in an average purity > 90% for both configurations. This experiment demonstrates the broad capabilities of WOLF G2 and highlights the potential sorting possibilities that are now achievable.
For more information, visit nanocellect.com or email [email protected]
APN- 029
